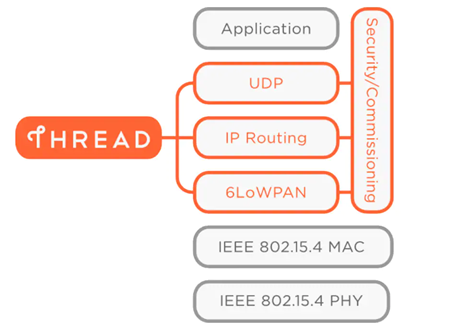
Any application layer which uses IP connectivity can run on top of the thread and this makes it really interesting because many building automation protocols like Bacnet over IP, KNX and DALI can now directly address Thread devices.
Thread is a low power, secure and IPv6 based mesh networking technology for home and commercial IoT products. This protocol was developed by Nest which was then acquired by Google. The Thread group alliance was formed in July 2014 as a working group to aid Thread in becoming an industry-standard by providing Thread certification for products. Thread is based on the 802.15.4 physical layer protocol and uses 6LowPAN for providing IP connectivity. The figure below shows the protocol stack for Thread.



